The concept of the Five Elements, or “Wu Xing” in Chinese, is a fundamental and deeply ingrained theory in traditional Chinese philosophy, culture, and science. It provides a framework for understanding the natural world, human body, and the dynamic relationships between different phenomena.
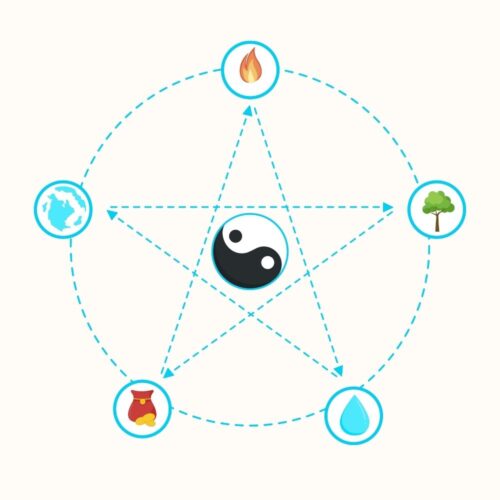
The Five Elements are Wood, Fire, Earth, Metal, and Water. Each element represents not only a physical substance but also a set of characteristics, functions, and qualities. Wood symbolizes growth, flexibility, and expansion, much like a tree that continuously grows and adapts. Fire embodies warmth, energy, and transformation, representing the power to change and evolve. Earth stands for stability, nourishment, and the center, signifying the foundation upon which life thrives. Metal represents clarity, precision, and the ability to cut or transform, while Water symbolizes adaptability, fluidity, and the source of life.
One of the key aspects of the Five Elements theory is the system of (mutual generation) and (mutual restriction). In the mutual generation cycle, Wood feeds Fire, Fire creates Earth (ash), Earth contains Metal, Metal conducts Water, and Water nourishes Wood. On the other hand, in the mutual restriction cycle, Wood can break through Earth, Earth can dam Water, Water can extinguish Fire, Fire can melt Metal, and Metal can cut Wood. This intricate web of relationships reflects the balance and harmony in the universe.
This theory extends far beyond abstract philosophy. In traditional Chinese medicine, the Five Elements are used to explain the functions of the body’s organs, the flow of Qi (vital energy), and the diagnosis and treatment of diseases. For example, the liver is associated with Wood, the heart with Fire, the spleen with Earth, the lungs with Metal, and the kidneys with Water. In Chinese astrology and feng shui, the Five Elements are used to analyze a person’s destiny, as well as to arrange living and working spaces to achieve optimal energy flow.
The Five Elements theory is a testament to the profound wisdom of the Chinese people. It offers a holistic view of the world, emphasizing the interconnectedness of all things and the importance of maintaining balance and harmony in life. Even in modern times, this ancient concept continues to inspire and influence various fields, bridging the gap between the past and the present.